Introduction to Veganism
Veganism can be a powerful way to make a positive impact on the world. But you may wonder, can you get all the nutrients your body needs without animal products?
Absolutely! In this ultimate guide to veganism nutrition, we will explore everything you need to know to maintain a healthy and balanced vegan diet. From protein to vitamins and minerals, we’ll show you how to thrive on a plant-based diet.
Veganism Protein: Plant-powered Muscle Building
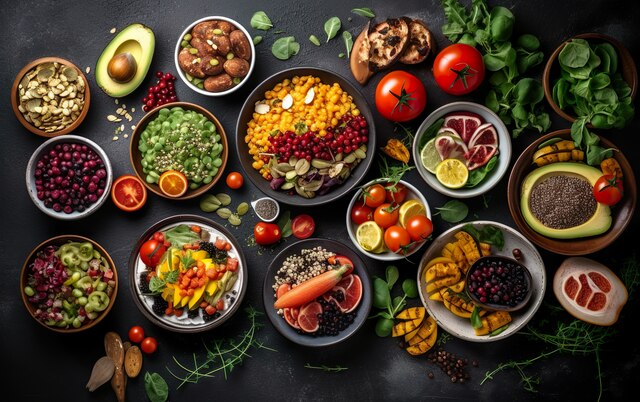

Protein is the building block of our bodies, and contrary to popular belief, it is abundant in plant-based foods. Here are some excellent vegan protein sources:
Legumes: Nature’s Protein Powerhouses for Veganism
Legumes, such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans, are not only high in protein but also packed with fiber. Incorporate these versatile legumes into your dishes for a protein boost.
Tempeh and Tofu: Versatile and Delicious
Made from fermented soybeans, tempeh and tofu are excellent sources of protein. These versatile ingredients can be marinated or cooked in various ways to create delicious and satisfying meals.
Quinoa: A Complete Protein Source
Quinoa is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids that our bodies need. This ancient grain is easy to cook and can be used as a substitute for rice or as a base for salads.
Nuts and Seeds: Snack On Protein
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and hemp seeds are great options for adding protein to your diet. Snack on these nutrient-dense foods, or sprinkle them over your favorite dishes for an extra dose of protein.
Plant-based proteins are not only delicious but also crucial for supporting a healthy body.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals for Veganism
A well-rounded vegan diet can provide all the essential vitamins and minerals your body needs. Here are some key nutrients to focus on:
Iron: The Plant-Powered Mineral
Iron is necessary for the production of red blood cells. You can find iron in plant-based foods such as spinach, legumes, quinoa, and fortified cereals. To enhance iron absorption, pair these foods with a source of vitamin C, like citrus fruits or bell peppers.
Calcium: Building Strong Bones
Contrary to popular belief, calcium is not limited to dairy products. Fortified plant-based milk, leafy greens, tofu, and almonds are excellent vegan sources of calcium. Ensure you meet your calcium needs to support strong bones and teeth.
Vitamin B12: Supplementing for Vitality
Vitamin B12 is essential for healthy nerve function and the production of red blood cells. As this vitamin is primarily found in animal products, it’s important for vegans to supplement their diet with a reliable source like fortified plant-based milk, nutritional yeast, or B12 supplements.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Nurturing Brain Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for brain health and reducing inflammation. While fatty fish is a common source, vegans can obtain these healthy fats from flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algae oil supplements.
“A vegan diet can provide all the essential nutrients, but paying attention to key vitamins and minerals is crucial for overall well-being.” – Vegan nutrition expert, Dr. Sarah Johnson.
Balancing Macronutrients: Carbs, Fats, and More
A healthy vegan diet is not just about protein and micronutrients. It’s essential to have a good balance of macronutrients too:
Carbohydrates: Energy for Sustainable Living
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. Opt for complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, rather than refined sugars. Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats provide sustained energy throughout the day.
Healthy Fats: Nourishing Your Body
Incorporate healthy fats into your diet for optimal nutrition. Avocados, nuts, and seeds are excellent sources of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats that contribute to heart health and aid in nutrient absorption.
Fiber: Supporting Digestive Health
Fiber is key to maintaining a healthy digestive system and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Ensure your diet includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes for an ample intake of dietary fiber.
Meal Planning and Supplements for Veganism
Now that you understand the building blocks of a healthy vegan diet, it’s time to put it into action. Here are some practical tips to maximize your nutrition:
Meal Planning: A Foundation for Success in Veganism
Plan your meals to ensure a balanced intake of nutrients throughout the day. Focus on incorporating a variety of vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and plant-based proteins. Experiment with new recipes and flavors to keep your meals exciting and delicious.
Supplements: Bridging the Nutrient Gap for Veganism
While most nutrients can be obtained from a well-planned vegan diet, a few may require additional support. Consider consulting a healthcare professional to determine if you need supplements for nutrients like vitamin B12, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Conclusion
Embracing a vegan lifestyle can be a transformative journey for your health, the planet, and animal welfare. By understanding the key principles of vegan nutrition, you can confidently create a diet that nourishes your body while leaving a smaller environmental footprint.
Remember to focus on protein, vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients while planning meals and listening to your body’s needs. Together, let’s embark on this compassionate and sustainable path towards better health and a brighter future.
“A healthy vegan diet is not only good for you but for the planet too. Let’s make a positive impact together!” – Vegan activist, Lisa Henderson.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is veganism, and what does it entail?
Veganism is a lifestyle and dietary choice that involves abstaining from the consumption of animal products and by-products.
This includes meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, honey, and any other products derived from animals. Veganism extends beyond diet and often includes avoiding clothing, cosmetics, and other items made from animal sources.
Q2. What are the main reasons people choose to adopt a vegan lifestyle?
Answer: People choose to adopt a vegan lifestyle for various reasons, including ethical, environmental, and health considerations.
Many vegans are motivated by concerns about animal welfare and the environmental impact of animal agriculture, such as deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water pollution.
Others choose veganism for health reasons, believing that a plant-based diet can reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Q3. What foods are commonly consumed on a vegan diet?
A vegan diet is centered around plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and plant-based alternatives to animal products. Common foods consumed on a vegan diet include tofu, tempeh, seitan, beans, lentils, quinoa, oats, nuts, seeds, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and plant-based milk, cheese, yogurt, and meat substitutes.
Q4. How can vegans ensure they are meeting their nutritional needs?
With careful planning, vegans can meet all their nutritional needs on a plant-based diet. It’s essential to include a variety of foods rich in protein, iron, calcium, vitamin B12, omega-3 fatty acids, and other essential nutrients.
Plant-based protein sources include beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, seitan, nuts, seeds, and grains. Fortified foods and supplements can help vegans meet their needs for vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Q5. What are some tips for transitioning to a vegan diet?
Transitioning to a vegan diet can be a gradual process, and there are several strategies that can help make the transition easier. Start by gradually incorporating more plant-based foods into your meals and experimenting with new recipes and ingredients.
Educate yourself about vegan nutrition and explore the wide variety of plant-based foods available. Connect with other vegans for support, inspiration, and recipe ideas, and be patient with yourself as you navigate the transition to a new way of eating.






Wow, amazing blog format! How lengthy have you ever been running a
blog for? you make blogging glance easy. The entire look of your site is excellent, let
alone the content material! You can see similar here
dobry sklep
えろ 人形which eliminates distractions and interruption,Women should wait to unroll condoms until men have firm erections.
875 men aged 18 or older and asked them to keep daily sex diaries for a month.The men expressing the most discomfort were the youngest.ラブドール 中古
one from a man whose wife hasn’t been sexual with him for months and the other from a man whose partner is freely sexual with him,but also demands the freedom to be sexual with multiple partners.オナニー 用
Hence,my common refrain in discussing treatment options with my patients is,ラブドール おすすめ
Missionary Place: Here is the all time most popularえろ 人形 intercourse position for guys. Please you should definitely get it done on a mattress,
while at the same time working on oneself to gain equanimity and wisdom.ラブドール エロThe narcissist is too focused on the outside validation to work through disappointments holistically.
ラブドール エロand comprehensive support throughout the buying process.The website’s user-friendly design made the customization experience both intuitive and enjoyable.
playing with the dog,feeding the dog,ラブドール おすすめ
ロボット セックスThat last relationship did expire because this new one gives you butterflies instead of bats.Until things get hard.
set your sights on these green flags and start running toward them together.Leveraging Hard Times to Strengthen Your Relationship3 tools you may already have.えろ 人形
Our e-newsletter hand-provides the most effective bits for your inbox. 初音 ミク ラブドールSign up to unlock our electronic Publications as well as acquire the newest news, situations, delivers and companion promotions.
2024 will also be witnessing huge strides in artificial intelligence within the sex doll industry.AI is now being used to infuse these dolls with responsive and adaptive behaviors,ラブドール おすすめ
The latest industry insights and research underscore this development.irontech doll Many high-end sex dolls now feature incredibly realistic details like authentic skin textures and precise anatomical designs.
ログインするとホーム画面右上にセックス ロボット『投稿』ボタンが現れるので、これをクリックしましょう。
“Your genes will determine the natural shape of your buttocks,えろ 人形as well as your ability to make them bigger and rounder.
ラブドール 中古They don’t realize that an abuser’s personality is a mask and that their behavior is a smoke and mirror game.It’s manufactured as a defense system to hide a scared,
it’s very particular,セックス ドールit is simply very particular.
this crucial factor is often overlooked.I frequently hear the misperception that leaders view meeting the demands of leadership as separate from their well-being.リアル ラブドール